Software
Python packages
chatter: a Python library for applying information theory and AI/ML models to animal communication
GitHub | Documentation | Paper

Historically, analyses of sequential structure in animal communication have involved the identification of unit types (e.g. "syllables" in bird song and "notes" in whale song). This collapses continuous variation into discrete categories that align with human perception, a process that loses a great deal of the complexity and nuance present in the actual signals. Recent innovations in machine learning, such as variational autoencoders and vision transformers, allow us to bypass discretization and analyze animal communication signals directly in continuous space. chatter makes it easy for researchers to apply these methods to their data, to quantify features like:
- Complexity—path length of sequences in latent space per unit time.
- Predictability—predictability of a transition in latent space.
- Similarity—cosine similarity between units or sequences in latent space.
- Novelty—inverse of predicted density of units or sequences in latent space.
R packages
TwitterABM: agent-based model of biased cultural transmission on Twitter
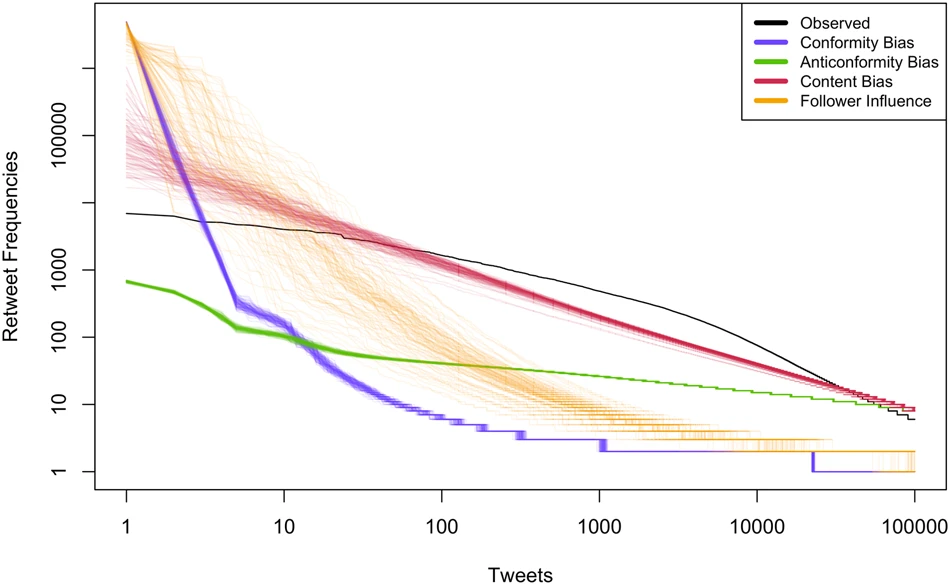
An agent-based model (ABM) for exploring how ideas spread on Twitter/X under different assumptions about why people copy what they see. It simulates three classic transmission biases—content (some messages are intrinsically more “catchy”), frequency (people copy what’s common), and demonstrator (people copy influential accounts)—so you can run controlled experiments and see which mechanisms reproduce real-world patterns. The model draws on Carrignon et al. (2019), Lachlan et al. (2018), and Youngblood & Lahti (2021).
DynCommPhylo: phylogenetic reconstruction via dynamic community detection

Tools for turning dynamic community structure in networks into something you can read like an evolutionary tree. DynCommPhylo takes the output of the TILES dynamic community detection algorithm, simplifies the network structure (via fast-greedy modularity optimization), and produces phylogeny-style plots that highlight splits, merges, and lineages over time—useful for tracking how communities evolve in social, cultural, or biological systems.
TransmissionBias: agent-based model of biased cultural transmission

An agent-based model (ABM) for simulating cultural evolution when learners acquire a repertoire of traits (e.g., birdsong syllables, musical motifs, behaviors). It implements three core transmission biases—content, frequency, and demonstrator—and extends the framework of Lachlan et al. (2018) to support dynamic population sizes, making it easier to explore realistic demographic change. The learning step is implemented in C++ (via Rcpp) for speed, so you can run large sweeps and sensitivity analyses efficiently (requires Rcpp + C++11).